栈的定义
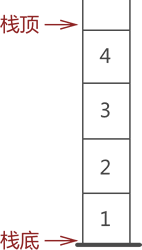
栈是一种只能从表的一端存取数据且遵循 “后进先出 LIFO(Last In First Out)” 原则的线性存储结构。

通常,栈的开口端被称为栈顶,允许进行插入和删除;相应地,封口端被称为栈底,不允许进行插入和删除。
基于栈结构的特点,在实际应用中,通常只会对栈执行以下两种操作:
- 向栈中添加元素,此过程被称为”进栈”(入栈或压栈);
- 从栈中提取出指定元素,此过程被称为”出栈”(或弹栈);
栈的基本操作:
void InitStack(SqStack &S); // 初始化一个空栈bool StackEmpty(SqStack S); // 判断一个栈是否为空, 若找 s 为空则返回 true,否则返回 false。bool Push(SqStack &S, ElemType x); // 进栈,若栈 s 未满,则将 x 压入栈bool Pop(SqStack &s, ElemType &x); // 出栈,若栈 S 非空,则弹出栈顶元素, 并用 x 返回。bool GetTop(SqStack S, ElemType &x);// 读栈顶元素,若栈 s 非空,则用 x 返回栈顶元素。void DestroyStack(SqStack&S); // 销毁栈,并释放栈 s 占用的存储空间。bool StackOverflow(SqStack S); // 判断栈是否满int StackLength(SqStack S); // 栈元素个数
栈的顺序存储
采用顺序存储结构可以模拟栈存储数据的特点,从而实现栈存储结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
|
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct SqStack {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top;
} SqStack;
void InitStack(SqStack &S){
S.top = -1;
};
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S){
return S.top == -1;
};
bool Push(SqStack &S, ElemType x){
if (StackOverflow(S)) {
return false;
}
S.data[++S.top] = x;
return true;
};
bool Pop(SqStack &S, ElemType &x){
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
return false;
}
x = S.data[S.top--];
return true;
};
bool GetTop(SqStack S, ElemType &x){
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
return false;
}
x = S.data[S.top];
return true;
};
void DestroyStack(SqStack &S){
S.top = -1;
free(S.data);
};
bool StackOverflow(SqStack S){
if (S.top >= MaxSize-1) {
return false;
}
};
int StackLength(SqStack S){
return S.top+1;
};
|
栈的链式存储
采用链式存储结构实现栈结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
typedef struct LinkNode {
ElemType data;
LinkNode * next;
}LinkNode, *LiStack;
LiStack InitLiStack(LiStack &LS){
LS = (LiStack) malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
LS->next = NULL;
return LS;
};
bool LiStackEmpty(LiStack LS){
return LS->next == NULL;
};
void LiPush(LiStack &LS, ElemType x){
LiStack Lhead = (LiStack) malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
Lhead->data = x;
Lhead->next = LS->next;
LS->next = Lhead;
};
ElemType LiPop(LiStack &LS){
if (LiStackEmpty(LS)) {
return false;
}
ElemType x;
LiStack Lhead = LS->next;
LS->next = Lhead->next;
x = Lhead->data;
free(Lhead);
return x;
};
int LiStackLength(LiStack LS){
int i = 0;
while (LS->next != NULL) {
i ++;
}
return i;
};
|





